You can buy different types of business insurance policies. But which ones work best for you? Continue reading to learn how each coverage operates.
However, the financial security that business insurance provides in the event of unanticipated mishaps and disasters is one of its greatest advantages. Having the appropriate policy is essential to accelerating your company’s recovery. But how can you tell which of the many company insurance policies available offers the right coverage?
Moreover, this article on different types of business insurance will assist you with this. This information may be useful if you’re a business owner attempting to choose which policies best suit your particular requirements. We will outline the many types of coverage available to you and the level of protection that each offers. Continue reading to discover the kinds of company insurance plans that are best for you.
Which kinds of business insurance coverage ought to be taken into account?
However, there are dangers and difficulties specific to your company that do not apply to other companies. Because of this, no one policy can satisfy every need.
Different types of business insurance providers offer a variety of plans that can better protect companies. There is a wide range of options, and the type of coverage you need will rely on several variables, such as location, size, and scope. These are a few of the most important kinds of business insurance coverage you require to maintain operations during mishaps and disasters.
1. Insurance for general liability
Businesses consider it crucial to carry general liability insurance, also known as public liability insurance or commercial liability insurance, even though it is not legally necessary. This insurance type offers essential protection, making it one of the most important coverages to have. It offers financial protection for your company against lawsuits alleging property damage and personal injury brought on by regular business operations.
Libel, slander, and privacy invasions are examples of events that might result in reputational injury and for which general liability policies may offer coverage.
The majority of policies also include product liability coverage, which shields your company from legal actions alleging damages or injuries stemming from goods you manufacture or sell.
General liability insurance covers the costs of both legal defense and settlement if your business inflicts the aforementioned injury. Certain policies also cover medical costs if someone is hurt on your property, regardless of whether you are at fault or if someone brings a lawsuit against you.
The kinds of enterprises that require general liability insurance are shown in the table below.

2. Insurance for business property
Commercial property insurance lessens the financial toll that natural and man-made calamities take on the physical assets located on your company’s premises. Among them are:
- Property or structure where your firm is located Technology and equipment used by your business
- Inventory of goods and commodities that your business sells and stores
By covering losses and damages, commercial property coverage helps to minimize the interruption that unforeseen events might cause to your regular business operations. Certain policies additionally compensate for a portion of lost earnings if the damage prevents your company from operating as usual. Commercial leasing agreements frequently require this kind of business insurance, even though it’s not necessary.
A business owner’s policy (BOP), a type of small business insurance, usually includes commercial property insurance in addition to general liability insurance. Business interruption coverage is also included in some BOPs.
3. Insurance for workers’ compensation
Workers’ compensation insurance shields your company from the financial burden of covering medical expenses for illnesses and injuries sustained on the job. In the US, almost every state mandates that companies with a specific workforce size have this kind of insurance.
You have full financial responsibility for the cost of coverage as the owner of the business. You are not allowe to make your staff pay a portion of the premiums.
There is no culpability in the workers’ compensation insurance system either. This implies that the carelessness of their or your company does not affect an employee’s benefit, but there are several circumstances in which the workers’ compensation claim may be reject.
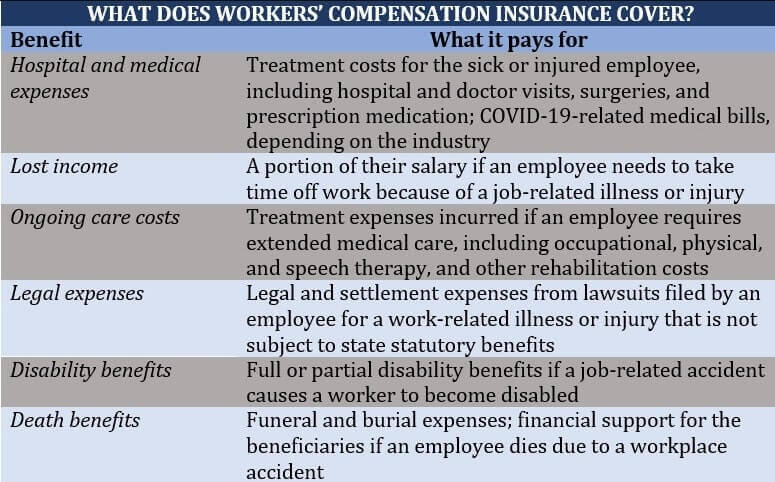
What is usually covered by workers’ compensation insurance is shown in the table below.
4. Insurance for commercial vehicles
One of the many forms of business insurance coverage that are mandated by law is commercial vehicle insurance. The primary distinction between this type of coverage and private auto insurance is that the former primarily covers company vehicles, as well as commercial trucks and vans.
The typical coverage for commercial car insurance is summarized in the table below.
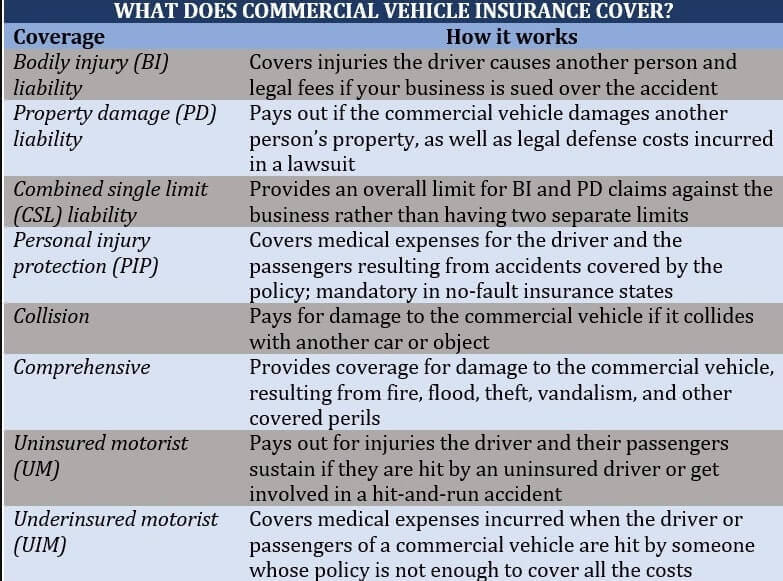
Businesses may acquire UM and UIM coverage independently in certain states. Additionally, coverages tailored to businesses are offered, such as those for lost business income.
5. Health insurance
The Affordable Care Act mandates that you obtain health insurance for your employees if your company has more than 50 full-time employees (ACA). You can use the Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) if you employ fewer than fifty people.
Health insurance intends to somewhat defray the expense of medical care by paying for some of the associated hospital and professional fees. The health policy-focused non-profit KFF conducted the most recent employee health benefits survey and found that US employers cover over 83% of their workers’ entire health insurance costs for single coverage and 72% for family coverage. The anticipated yearly values for these are $7,911 and $22,463, respectively.
6. Insurance for professional liability
Businesses providing expert or advisory services find it necessary to have professional liability insurance, even if it’s not usually mandated by law.
Professional liability insurance shields your company from lawsuits alleging financial losses stemming from purported or proven carelessness in the course of providing a professional service. It pays for settlement and legal expenses related to the following:
- Errors and omissions in the service
- Erroneous guidance
- False representation
- Violation of the agreement
- Incomplete tasks
- Overspending on the budget
- Personal harm, such as slander and libel
In certain professions, professional liability insurance is required. It may also be known as malpractice insurance or errors and omissions (E&O) insurance, depending on the sector.
Some of the occupations where this kind of coverage is necessary are included in the table below:
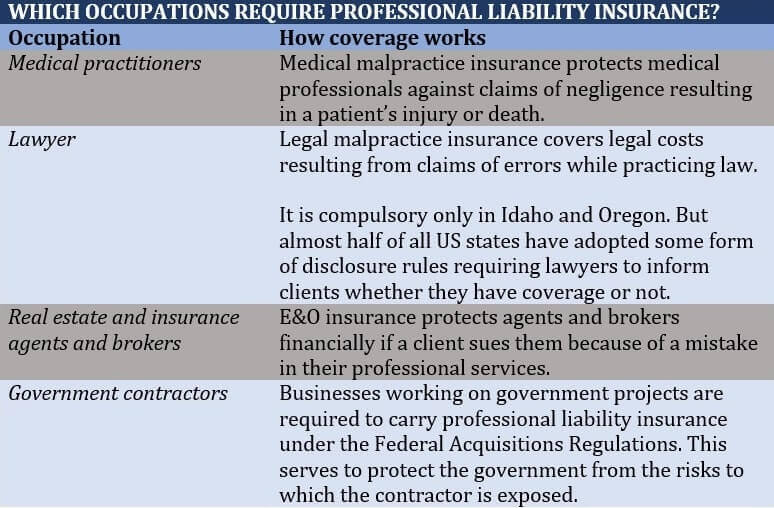
The following occupations can profit from professional liability insurance, while it’s not required:
- Accountants, Architects
- Advisors
- Engineers
- Advisors on finances
- Designers of graphics
- Experts in information technology (IT)
- Experts in insurance
- Attorneys
- Physicians
- Real estate experts
- Programmers
- Artists
- Artisans
- Planners of weddings
7. Insurance for directors and officers (D&O)
D&O insurance is intended to shield your company’s directors and senior management against monetary damages brought on by lawsuits about your organization. It also pays for financial losses resulting from these legal actions and is also known as D&O liability coverage. These consist of fines as well as settlement and defense expenses.
D&O coverage comes in three primary varieties. These are sometimes known as insurance sides or agreements, and each one offers a distinct degree of security.
- Side A: Provides coverage for “non-indemnifiable loss” or circumstances in which your business is unable to reimburse its officers or directors. This may be the result of bankruptcy or the inability of your company to operate legally.
- Side B: Pays back your company once it has made a loss-related payment to a director or other senior management. The most accessed insurance policy is this one.
- Side C: Offers direct coverage to a corporation if a lawsuit names not only your business but also its directors and senior management. Another name for this policy is entity coverage.
8. Online liability protection
The purpose of cyber insurance is to protect against monetary losses brought on by online occurrences. Businesses are increasingly using this type of coverage as a risk management tool, particularly in light of the rapidly growing cyber dangers that have arisen due to the quick drive to digital transformation.
Generally speaking, cyber insurance provides two kinds of security:
1. Coverage by first parties
This kind of coverage reimburses your company for any monetary losses brought on by a cyberattack, such as:
- The price of handling a data leak
- Data restoration and recovery from lost or corrupted
- Payments for ransomware attacks
- Income lost as a result of a company disruption
- Evaluation of future cyberattack risks
- The price of informing customers about the cyber event
- The price of offering anti-fraud services to a customer
2. Coverage by third parties
This kind of coverage offers monetary defense against claims brought by other parties for losses incurred by their companies as a result of a cyberattack. These could consist of your clients, suppliers, and even staff members.
Cyber liability coverage is another term for third-party plans. Typically, it pays fines and regulatory costs in addition to court and settlement fees.
9. Insurance against business interruption
Business interruption insurance, also known as BI coverage, covers the financial losses your company incurs when it experiences a disruption due to an insured incident. This insurance covers your business’s operational expenses in the event of a temporary closure. Among these expenses are:
- Potential income Salary of employees
- Repayment of business loans
- Rent or mortgage on a business property
- Taxes
Certain BI insurance also covers additional costs associated with the closure. These consist of the price of putting up a temporary facility or teaching employees how to use new machinery. There are situations when a business owner’s policy includes BI coverage.
After a 48–72-hour waiting period, you must activate insurance against business interruption. The restoration period of your insurance, which has a 30-day initial term and a one-year maximum extension, specifies this requirement.
10. Insurance for tools and equipment
“Tools and equipment insurance” actively covers the costs of replacing and repairing your company’s tools and equipment in the event of loss, theft, or vandalism. If your company depends significantly on its tools and equipment to complete tasks, you should think about getting this kind of coverage.
If you meet the following three requirements, this policy will cover a broad variety of products and equipment that you use for your business.
- They can be move.
- Their ages do not exceed five years.
- Their value is under $10,000.
Insurers frequently write insurance for tools and equipment on an all-risks basis. This implies that it might cover things not expressly mentioned in your policy. Certain insurance offer protection for the tools and equipment you rent or lease. Policies that reimburse for missed wages and extra materials or services required to complete the job on time are also available.
11. Insurance for product liability
If your company creates, produces, or markets goods, it would be wise to look into purchasing product liability insurance. This kind of business insurance shields your business from lawsuits that clients bring, alleging they suffered harm or losses as a result of your product. If the company is determine to be at fault, it also covers defense expenses and damages.
12. Insurance that covers excess responsibility
Excess liability insurance protects your company from catastrophic claims and losses that exceed the limits of your policy. This kind of insurance can assist reduce the likelihood that a lawsuit or other calamity will force your small business to file for bankruptcy if you are a business owner. Additionally, some companies require this kind of coverage as a requirement for a customer contract or lease. Another name for excess liability insurance is commercial umbrella liability insurance.
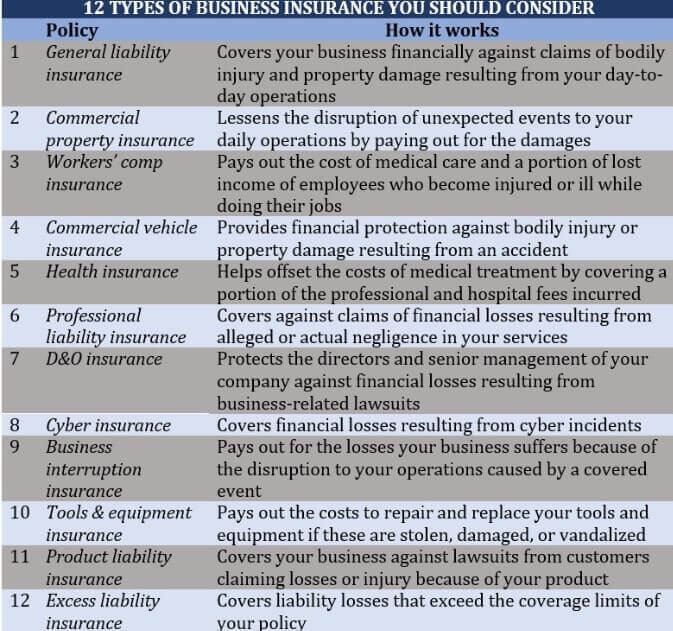
The 12 different business insurance policy kinds that any company should think about are summarize as follows:
Conclusion
Your company may encounter circumstances in the course of daily operations that could negatively impact your profitability. Errors may result in expensive legal actions, and disasters may significantly reduce earnings. The appropriate kinds of business insurance coverage can assist in giving you the necessary financial security in the event of unforeseen catastrophes.
Moreover, having the appropriate kinds of business insurance also improves your company’s reputation. The rationale is that many clients and stakeholders favor doing business with companies they are certain to be financially secure.
However, obtaining coverage is only one way to reduce the damages to your company. The greatest strategy to safeguard the resources and cash of your company is frequently to combine effective risk management techniques with the appropriate insurance coverage.